DNA Promiscuity Test
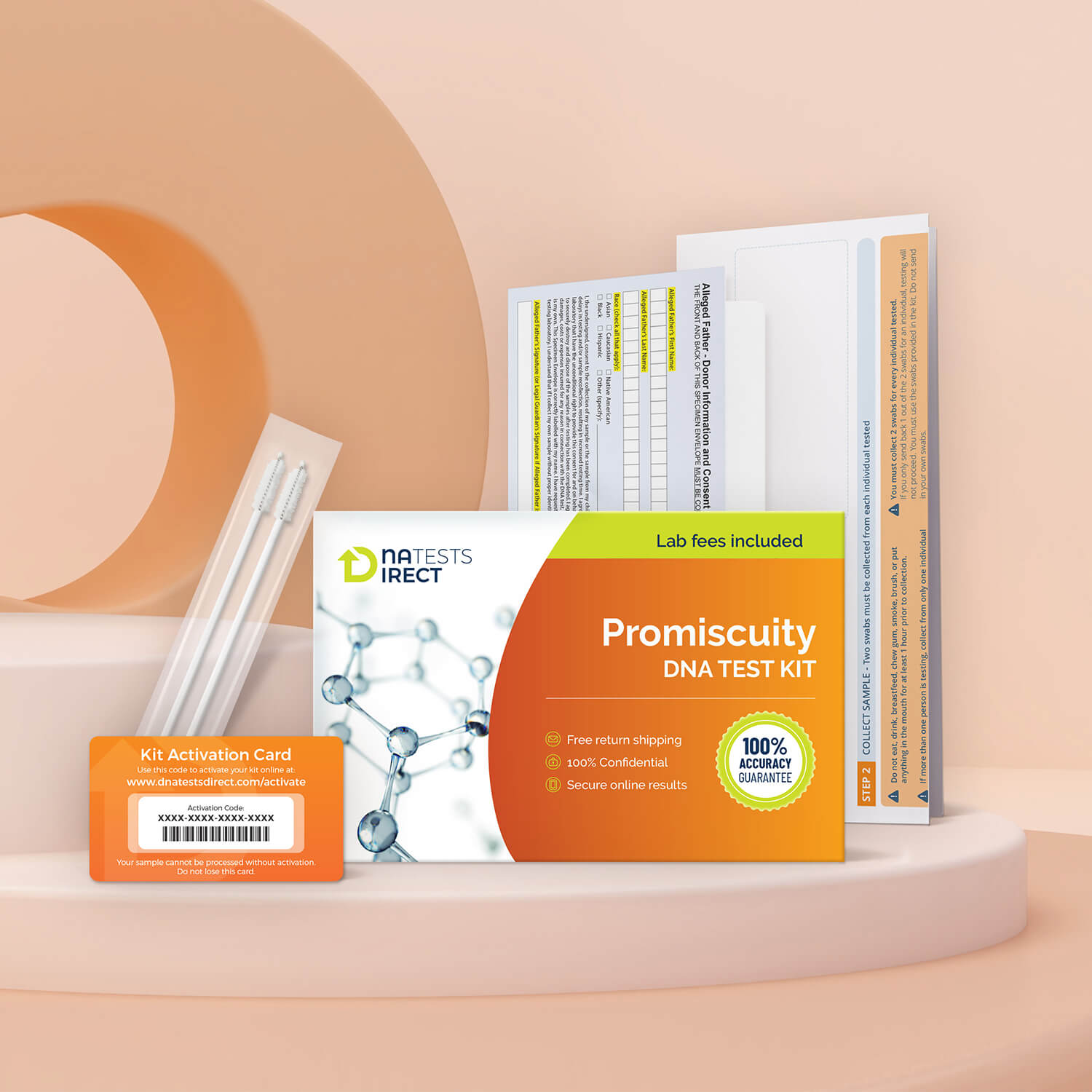
DNA Promiscuity TestDNA Promiscuity Test
$149
What is the “promiscuity” gene?
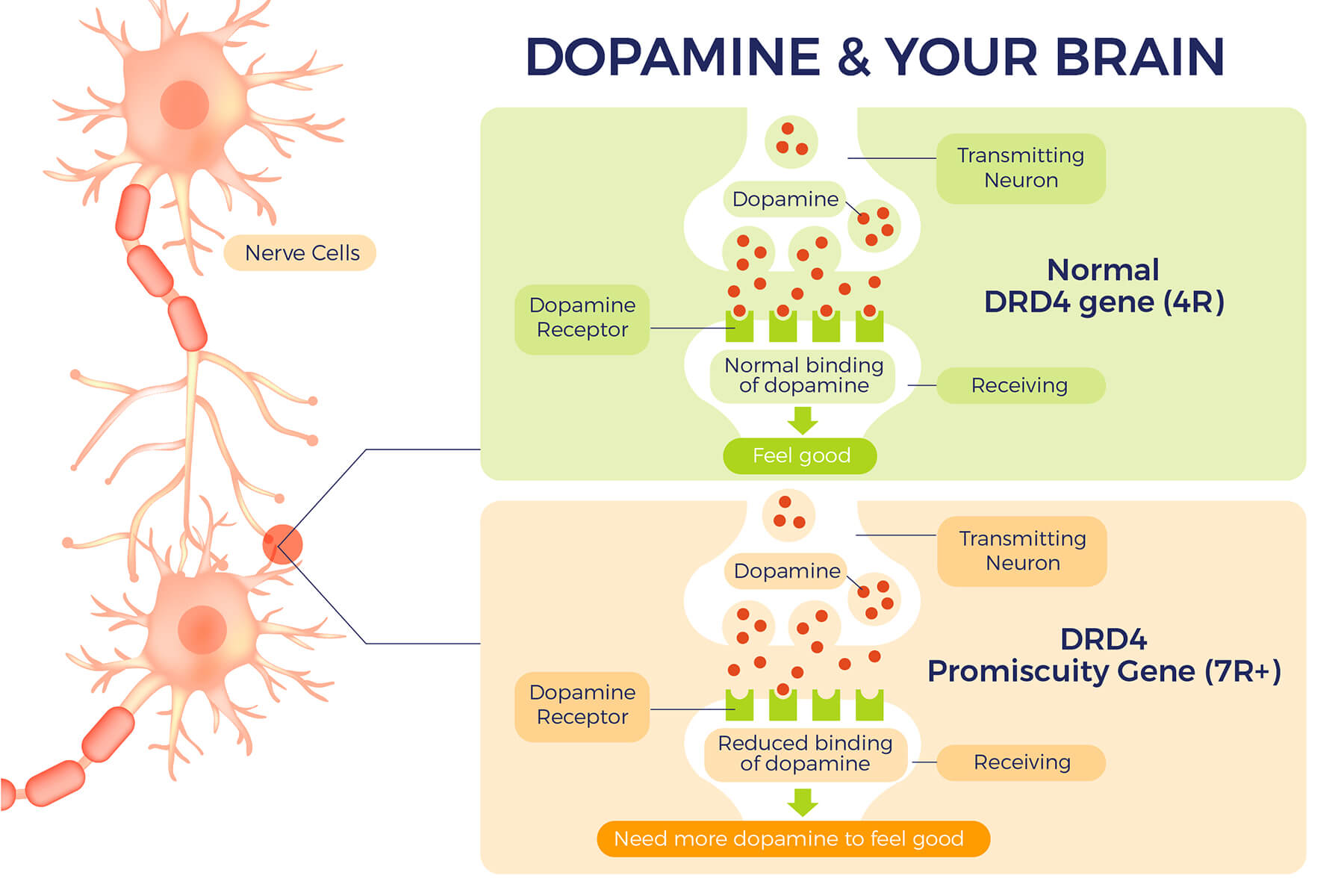
The “promiscuity” gene is a genetic variant of the DRD4 gene that is associated with an increased likelihood of sexual promiscuity. This variant is also known as the 7R+ version of the dopamine receptor and binds dopamine less efficiently compared to the common 4R version. As a result, reduced levels of the dopamine “feel good” signal is transmitted in the brain. Individuals with the 7R+ variant require higher levels of dopamine to achieve the same “good feeling” affects, and intriguingly sexual activity is a proven way to increase dopamine levels.
- Online Results: Receive confidential results through a secure online portal, ensuring your privacy and peace of mind at every step.
- Painless Sampling: Collect your DNA samples with easy-to-use mouth swabs – no blood or needles required.
How It Works

Order
Send
Receive your results

Results
How is the “promiscuity” gene inherited?
The DRD4 gene is located on chromosome 11. Variation in the DRD4 gene often occurs in a repeat region, where the number of repeats of a 48-bp segment ranges from 2 – 11. We inherit two copies of the DRD4 gene – one from each parent. We can inherit two identical copies (e.g. both 4R) or two different copies (e.g. 4R and 7R). Inheriting a “promiscuity” variant (7R+) is associated with increased promiscuity and an increased number of extra-pair partners.
What is the AVPR1A Gene?
The AVPR1A gene encodes the arginine vasopressin receptor 1A, which plays a crucial role in transmitting signals from the hormone vasopressin into cells. Vasopressin helps regulate water retention in the kidneys and increases blood pressure when released into the bloodstream. However, when released directly into the brain, it can also influence social and sexual behaviors, including bonding and fidelity. Genetic variations in AVPR1A have been linked to an increased likelihood of extramarital relationships or extrapair mating, sometimes referred to as the “female infidelity gene.
Conditions Linked to the AVPR1A Gene
Genetic variations in the AVPR1A gene have been associated with a higher likelihood of infidelity in both men and women. Additionally, other variations in this gene have been connected to:
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Altruistic behavior
- Addiction tendencies
- Eating disorders
- Social behaviors, including sibling interactions
Frequently Asked Questions
Once your sample is received by our laboratory, processing usually takes 6-8 weeks. You will receive an email notification when your results are ready, and you can access your detailed report through a secure online portal.
We take data privacy seriously. Your results are confidential and only shared with you. We do not share your results with insurance companies, employers, or any other third parties.
Why DNA Tests Direct?
Accredited Excellence
Your Privacy, Protected
Expert Support
Related Test Kits
$149
Do your genes play a role in how you feel? This test reveals how your DNA might affect your mood, stress levels, and risk for anxiety and depression.
$498
Unlock your genetic potential for a healthier lifestyle with our comprehensive DNA Diet & Fitness 3 Test Combo. This bundle combines three powerful tests – Nutrition, Fitness, and Weight Loss – to provide a complete picture of how your unique DNA influences your overall health and wellness.
$249
Discover your natural strengths, optimize workout strategies, and reduce injury risk with our DNA Fitness Test. This simple, at-home DNA test provides insights into your endurance, power, muscle mass, and physical response to exercise.
$349
Heart health is influenced by genetics because genes influence the levels of “good” cholesterol, “bad” cholesterol and triglycerides. Find out if you are at increased risk of poor heart health.
$149
Understand your body’s unique ability to break down lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Our easy-to-use test analyzes your DNA for key genetic markers associated with lactose tolerance and intolerance.
$149
Is caffeine your friend or foe? Our simple DNA test reveals if you’re a fast or slow caffeine metabolizer, so you can adjust your intake and feel your best.
$149 $271
Find out the likelihood that two people are biologically related as first cousins.
$149 $271
Confirm whether a potential mother is the true biological mother of a child.